Gas springs play a crucial role in motion control in everything from vehicles to industrial machinery. In this guide, we will explain how gas springs work, their components, and how to use them optimally.
What is a Gas Spring?
A gas spring is a spring that uses compressed gas to create and control motion. It typically consists of a cylinder filled with nitrogen gas and a piston rod filled with oil that moves through the cylinder. Gas springs are an efficient alternative to traditional coil springs because they offer: • Smooth and precise motion • High force in compact dimensions • Reduced maintenance requirements
Components of a Gas Spring
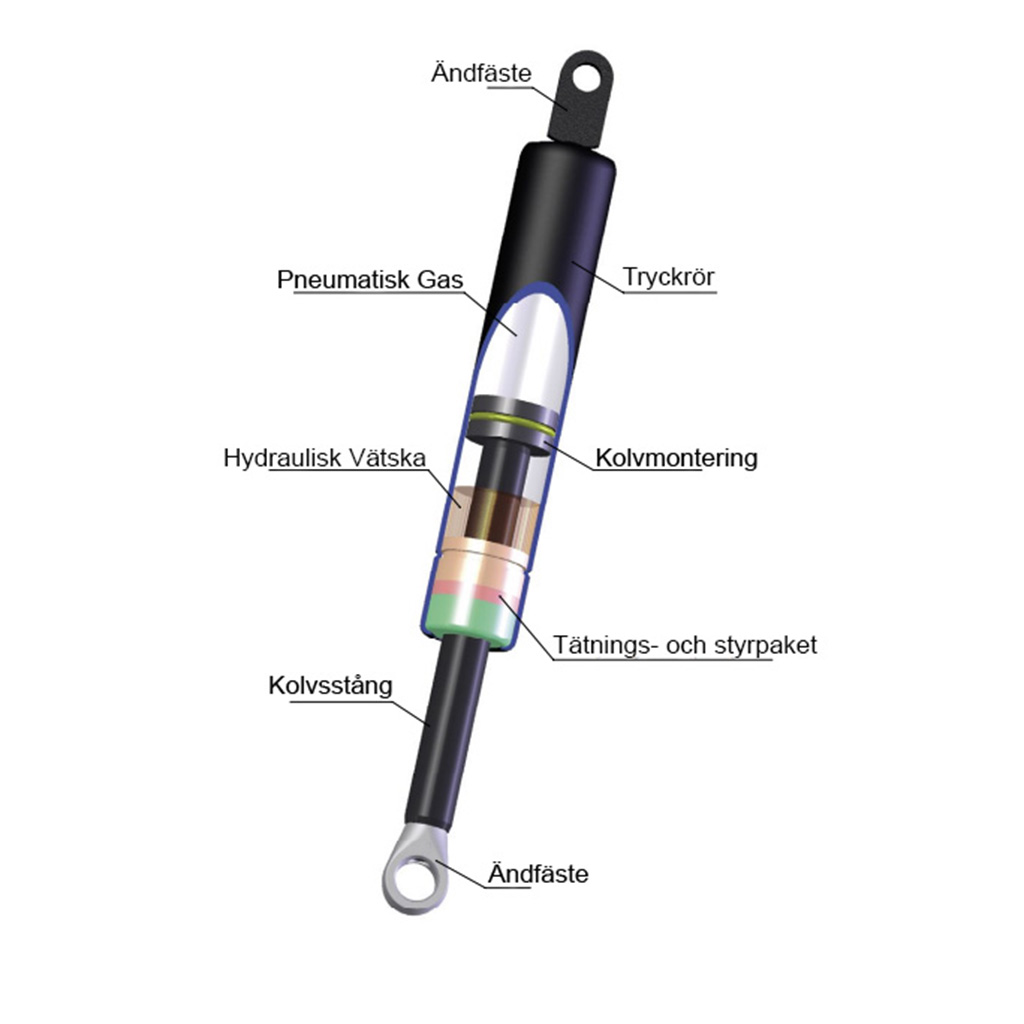
To understand how gas springs work, it is essential to know their main components: 1. Cylinder – Stores the compressed gas. 2. Piston and Piston Rod – The piston creates movement inside the cylinder, while the piston rod transmits the force outward. 3. Seals – Ensure tightness to prevent leakage. 4. Gas (Nitrogen) – Provides the pressure that drives the piston. 5. Oil Chamber – Lubricates moving parts and dampens impact at end positions.
How Do Gas Springs Work?
A gas spring works by using compressed gas in the cylinder to create pressure that drives the piston and piston rod outward. When the piston rod is pushed back, the gas compresses further, generating a return force. Step-by-Step Process: 1. The piston rod is pushed into the cylinder. 2. The gas compresses, creating counterforce. 3. The oil lubricates and dampens the motion as needed. 4. When the pressure decreases, the piston rod moves back outward.
Applications of Gas Springs
Gas springs are used in a wide range of applications thanks to their versatility and ability to deliver force in a controlled manner: • Automotive: Hoods, trunks, and tailgates. • Furniture: Office chairs and height-adjustable desks. • Medical: Hospital beds and adjustable care products. • Industry: Machinery and assembly lines. Example: In the automotive industry, Flexfill gas springs are used to create controlled and stable motion for trunk lids.

Advantages of Gas Springs Compared to Mechanical Springs
• Smooth Motion: Provides softer and more controlled movement. • Compact Design: Delivers high force in a small form. • Longer Lifespan: Less wear due to lubrication and damping. • Flexibility: Easy to customize for specific requirements.
Calculation Example: How to Dimension a Gas Spring
To select the right gas spring, you need to consider: 1. The weight of the object you want to support. 2. Length and stroke. 3. Mounting position. Force Calculation Formula: • F = Force in Newtons • W = Weight in kg • L = Length of lever arm in meters • S = Stroke in meters Tip: Use our Flexfill configurator to quickly find the perfect gas spring for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions about Gas Springs (FAQ)
1. How long does a gas spring last? A gas spring can last for several years, depending on usage and maintenance. 2. Can a gas spring be repaired? No, gas springs are typically sealed systems and should be replaced if faulty. 3. How should gas springs be stored? Store them in a horizontal position to prevent oil leakage.

FlexFill™ - Real Flexibility
With Aero Materiel’s FlexFill™ service, you get gas springs where the pressure is adapted to your application and your customers’ requirements. The gas springs can be ordered with different forces from 50 N up to 1800 N in different variants depending on the type of hatch they are to be adapted to. FlexFill™ is designed to be easy and affordable to order even a smaller number of gas springs, with the pressure you desire.
Benefits of FlexFill™
• Delivery within 48h directly from Jönköping • Opportunity to get the gas springs with your own printed label • Flexible products and competitive prices by stocking basic variants and adjusting the force • Quick and easy access to prototypes for testing and development needs Benefits of gas springs • Smooth and controlled movement • Long lifespan and maintenance-free • Can be adapted for different force and speed
Go to our gas spring configurator here!

